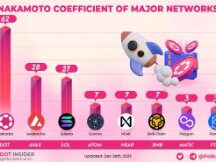
Why the DOT Token Design is Sustainable and Maximizes Community Benefits

According to a new study on pragmatic tokens from the Web3 Foundation research team, unlike core web2 platforms that focus on platform quality, decentralized pragmatic token ecosystems generally work best to deliver the best. services to anyone involved in the ecosystem. The study also highlights the collision of "symbolic ideas cannot be a triangle" and proves that the pragmatic Polkadot token model is safe for all participating communities that can achieve good state.
According to a statement released by FINMA in February 2018, electronic tokens are "tokens designed to provide digital access to a blockchain-based infrastructure application or service."
The services provided by PolkaDOT include Parachain locations that share security and means of communication with other Parachains on the network. To win any of these slot machines, the user (a group created by Polkadot) must commit to participating in the current DOT tournament.
For many functions based on the use of electronic tokens, it is common for each token to be unique on its own blockchain. This means that these tokens are needed not only to access the services, but also to support the nodes in the network in order to provide optimal services. These two roles also address design issues discussed in the recent research paper "Practical Token Design" (https://ssrn.com/abstract=3954773).
In this article, we have identified the equivalent equations of the first pragmatic proof of stake blockchain token. In the past, dynamic general equilibrium models have been used to describe the relationship between materials and requirements across industry. Token marketing and the industry as a whole have specialist users, developers (usually network nodes that "create" blockchain security), and support, so there are some similarities.
I saw the importance of the principle of entry tokens from two angles. First of all, we find that token systems are generally very functional because they improve the interaction between services. Second, we find inconsistencies between the main points of token value, the exchange rate of the services provided and the content of user incentives.
Samples
This explains the principle of using the token ecosystem. Readers dissatisfied with the intellectual content can skip ahead to discussing the findings in the next section.
I made a dynamic model of a token that can be used on an interactive platform. The platform is a specialized marketplace that aims to bring together different types of business participants to leverage the benefits of the network. Existing platforms include UBER (driver-passenger) and Amazon Marketplace (give-compare).
In my model, the platform is responsible for the development and management of software (commonly referred to as runtime in blockchain terminology) that needs to be maintained and run by the end user. To cover the cost of this operation, the platform would have to resell electronics in the store.
One thing I can think of is that the platform has a constant number of users and uses more tokens to consume certain resources. Meals are competitive and items are received from a single user bonus for sharing all tokens provided by each user. Basically all blockchain networks have limits, but the more tokens you hold, the more certain services you will get, such as the Parachain Polkadot Slots.
On the other hand, there is a stable number that needs to be resold part of their gifts in order to benefit from security and payment. However, validators may not want to provide all of their tokens. It faces trade as the distribution of rewards increases the total share of token possession of each user. This demonstrates the proof-of-stake potential of blockchain. The rewards you receive as a validator are proportional to your network share.
This model assumes that the symbolic ecosystem is in long-term equilibrium. This means that the number of network participants stays the same over time and there is no need to think about using tokens. In other words, tokens are only used to consume platform resources.
The pragmatic token value plays an important role in this situation because it has to balance the support between user and user. If today's price is too high for tomorrow's price, users will only buy a few tokens to enjoy the service, consumers will not be able to afford the cost of the process, and the network will collapse. On the other hand, if the price today is too low for the price tomorrow, consumers will not be able to make enough money by selling their tokens. If users expect the value of the blockchain service to increase rapidly over time, its value may increase further. Blockchain platforms will cost more to maintain the blockchain in the future and therefore lose value if more tokens are to be sold.
The platform has many options that affect the supply and demand for tokens. First of all, you can configure the profit agreement that is given for each contest. Second, you can improve the power consumption of users by providing quality services. Third, the platform can determine whether the tokens the user will use are binding (e.g. come back after every match, as in Polkadot) or use (deducted from tokens) the tokens held by the user, as in many smart contracts. ).
The balance of this setup is the token value and sharing performance between user, user device, and platform. Each balance must have a committed percentage, which is a proof-of-stake blockchain requirement for security.
to look for
The most important conclusion is that even though the blockchain platform has been modeled specifically on both the user and the side validator (i.e. it does not face competition from 'other platforms), there is always competition for the best option. level of service. In other words, by choosing the best level of service for everyone, the best level of platform selection is also the best for everyone.
Given our knowledge of usual quantum processes, this discovery may come as a surprise. Most of the duplex platforms include UBER, Amazon, and the iOS App Store. All of these platforms match the company's two terminals (driver and passenger, merchants and consumers, manufacturers and users) to generate revenue through network interference. However, it's usually not on the platform like to know all the perks. Exchange, it is well known that platforms affect the cost and / or quantity of services, thus maximizing platform profits while reducing the health of platform participants.
However, if you are aware of the benefits of decentralization, it should come as no surprise that electronic token devices are becoming more profitable. A unique feature of the electronic token is that the price of the service is not fixed by the contract, but rather competitively priced by the users. In Polkadot, the number of tokens required to earn a Parachain is decided in an offer, and in Ethereum, additional user information in the market decides the speed of trading in a block.
As long as the platform does not affect the cost of the services, it will try to make the best choice among the best services it provides. The main purpose of the article is to show that there is similar competition. Technically, this is achieved by creating a balance between the consumer and the consumer. In such a scheme, validators and users control their decisions using tokens so that their utility bills don't fluctuate between quality services. Maximizes overall health.
The second largest shape in the article is a "conceptual token impossible triangle" that describes a set of equilibria. A triangle cannot be defined because only two of the three characteristics can be equated: (i) a commitment on user tokens, (ii) a constant token value, and (iii) a fixed token value within services provided.
Intuitively, if functions (ii) and (iii) are true, then the best number of tokens the user has today is equal to the number of tokens the user wants to keep tomorrow. Now, if it is greater than that, if the user saves the token after eating (which is the result of activation (i)), the user will not need the token. However, this in turn means that no validator or blockchain platform is profitable.
This effect means that in practice you can expect to have more than two of the three characteristics in the actual design. A design with all three features will not work. However, by the actual design of the finder tokens, each of these operations may have its own unique value.
First, consider the cost of security. Over time, the reduced fares can be affected to some extent by improving the quality of service or by allowing certain users to withdraw tokens from the circuit anywhere. However, from a practical point of view, the economic model based on price stability is attractive. It's certainly more appealing than a well-known platform that constantly dilutes the amount of tokens.
Second, consider a symbolic seal. Bind a string when using a token user to consume the service and return it later. This way, their confidence will not fade over time and users will better understand what they can do with their tokens. Additionally, binding tokens can be used to swap contracts and, like contract tokens, linked tokens participate directly in the ecosystem on behalf of their owners, reducing token drainage around which is key. of security. .
Finally, think about service regularly. It is natural for many projects to have a constant value blockchain. An industrial model that relies on the downside decision can raise questions, but an industrial model that relies on blockchain inflation can also create security concerns. . In particular, people may fear that the cost of providing better services has risen rapidly to stabilize.
Relationship with Polkadot
The main conclusion from the above results is that the general structure of Polkadot is stable. The value of the token indicates the services that DOT can purchase. The token request created by the Parachain auction is based on the consumer's use to control the transaction.
Another general consideration is that you don't have to worry about a decentralized platform like Polkadot damaging your energy. Here's why: These platforms are unable to report competitive price protection behavior because they allow users to compete with each other without setting a specific price for their services. So the question is whether the platform will provide poor service. Examination of the table indicates that the answer is incorrect. Specifically, this article shows that there is an equation that the best choice of services is similar to maximizing the value of the platform.
Now it is clear that Polkadot does not have a platform designer, but it is community driven and has a clear management process. This is abstract from the model, but the conclusion still holds. The developers of the platform can be seen as software developers, a third party of actors who, together with users and users, decide to further improve the services and use of community decision making software. Reviews show that the developer's overall goals are in line with the user and the user's goal of having a positive impact on the community. Of course, the distribution of the balance between the different stakeholders depends on the management.
One indication that Polkadot is providing consumers and consumers with more incentives than necessary to provide adequate physical support is the use of binding procedures for Parachain auction bids. Analysis of the report shows that the best platform fairness (i.e. the platform profit maximization equation) does not include the binding of user tokens. (This is because when users' tokens are attached more than they eat, user demands for tokens are reduced, which is bad news for platforms that want to sell their tokens.) So Polkadot must be in contact with the platform. The best balance is another balance. However, this means that Polkadot's added value has been better placed with the community.

Scan QR code with WeChat